What is Global SEO?
Global SEO means optimizing your content for different regions around the world.
The main takeaway is that you'll need to create content that works for different regions and languages, as well as optimize that content for each region's most popular search engine.
For instance, search results appear differently for Italians using “google.it” and South Africans using “google.co.za.”
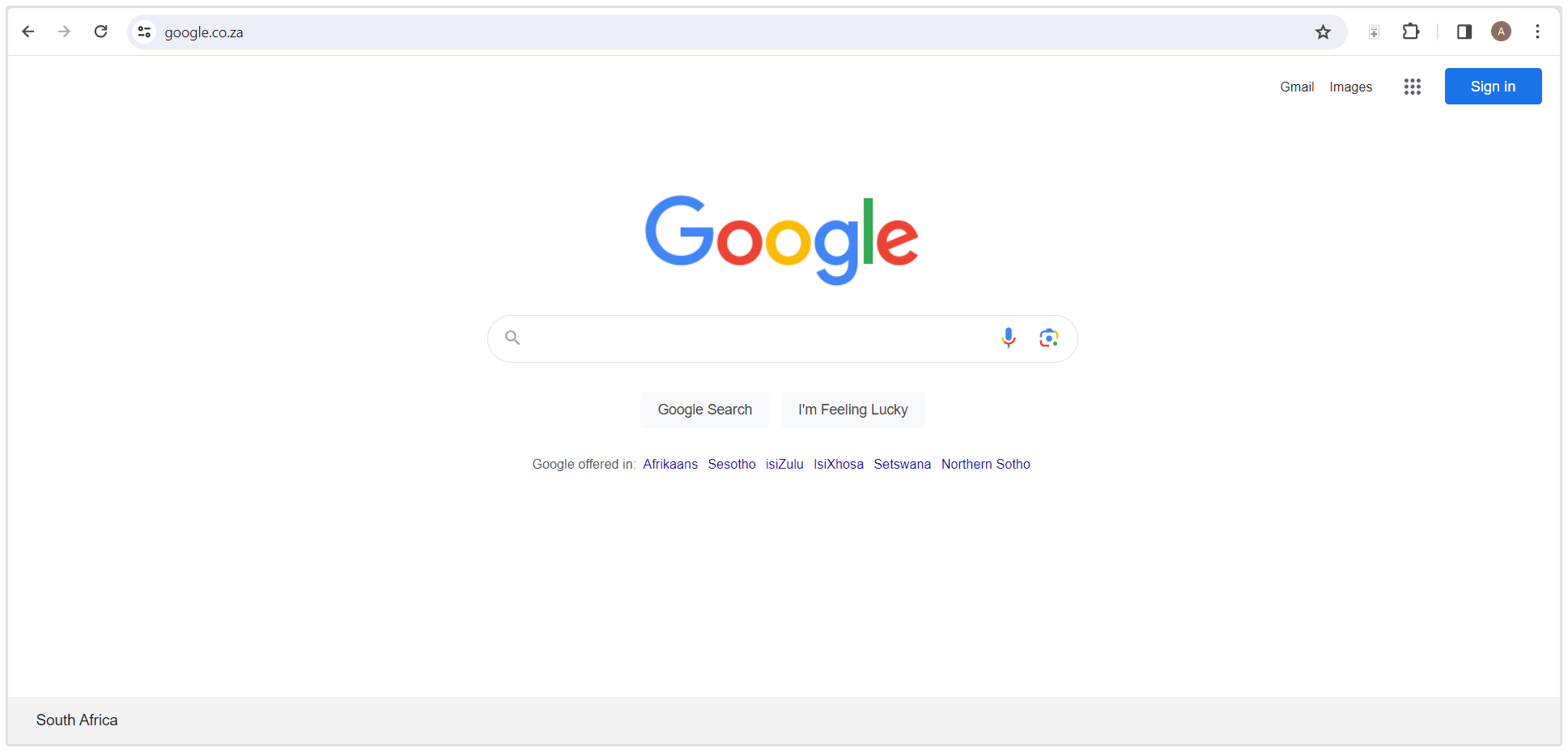
Let's say you sell strawberries and you have stores or business operations in Russia, Spain, France and Japan, but your local market is the UK.
Your global SEO would optimize for those countries as well as the word "strawberry" in the individual languages.
What is the Difference between Global SEO and Local SEO?
Local SEO is typically for offline businesses with a brick-and-mortar presence in a given city, state or country, whereas global SEO targets audiences across the globe.
For local SEO, Google relies on customer reviews, local directories and business information networks for local search rankings.
In global SEO, you need to optimize for different languages, cultures, and behavioral tendencies in your marketing messages and methods.
There are some global SEO tactics that are more general, like translating existing content into a variety of languages.
A word of caution: There are some people who might think, ‘Oh, I'll just automatically translate all my content into 40 different languages. Now 40 different language markets can read what I have to say.’
- Matt Cutts, Former Head of Google’s Webspam Team
And then to some extent, it's a matter of repeating local SEO over and over, until you've covered every specific region of interest.
It’s important to note that even though you’re targeting different countries and languages with global SEO, you still need to optimize and think of all the elements in general SEO.
Whether you serve a local or global market, you'll always have to put these general SEO practices in place.
This includes:
- Site speed
- Keyword optimization
- Backlinks
- Sitemaps
- User experience and Core Web Vitals
- Schema markup
1. Assess the Potential for Global SEO Expansion
Different industries have unique strengths and weaknesses. Some markets are more mature for specific products and services than others.
Your goal is to find the countries where your opportunities are most substantial and then pour your attention and resources in that direction.
Using your site traffic and competitor reports you can look at things like:
- What countries send you the most international traffic?
- What countries are converting the most in your marketing funnel?
- Who's showing the most interest in your products but can't access them yet?
- What markets are your competitors entering or planning to open in and why?
The idea is to gather intelligence, and then make informed decisions based on the data you have.
At the end of this research, you should be able to decide which countries have the most lucrative opportunities.
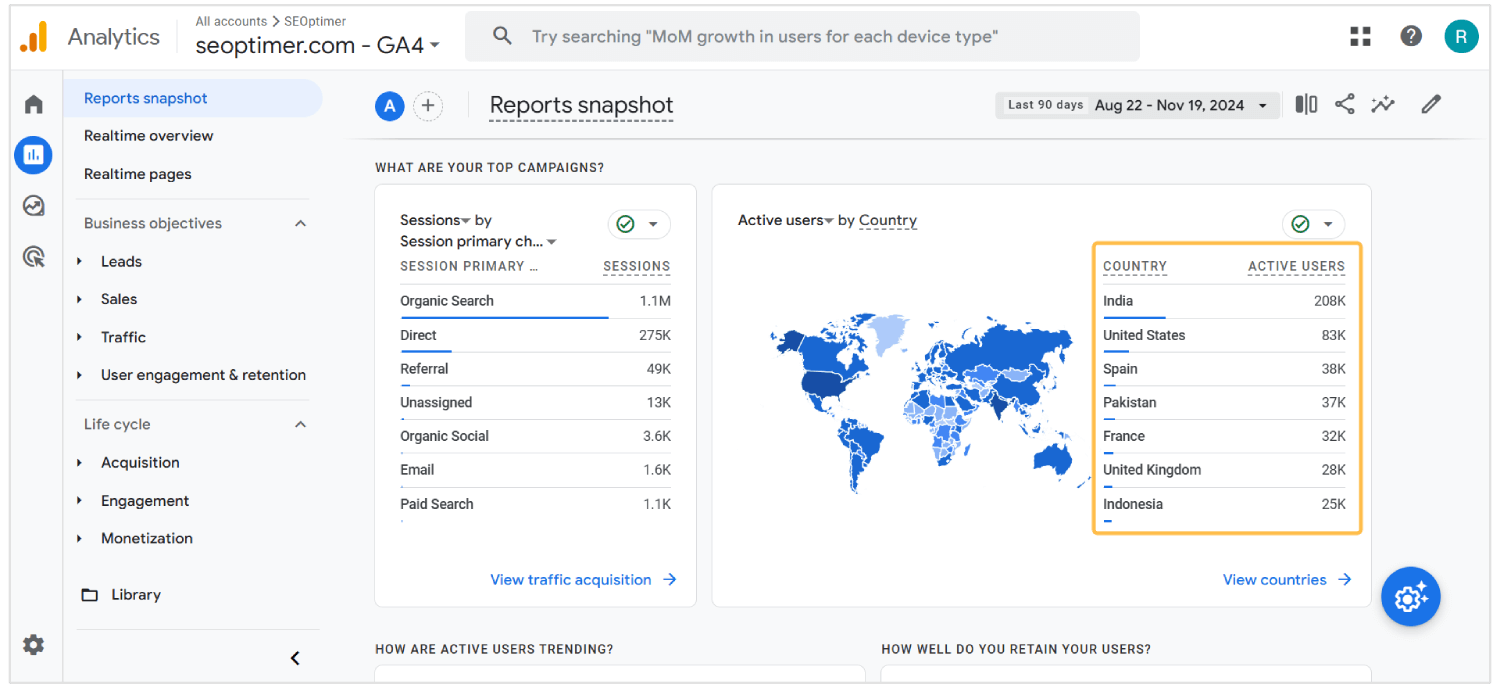
You can find a lot of the data of the countries sending you the most traffic and leads using Google Analytics.
For instance, check the screenshot of our Top Countries report in Google Analytics. By the looks of it, it would be ideal to focus on countries like India, Pakistan, United Kingdom, and Indonesia for our global SEO expansion.
2. Set Global SEO Goals
Once you've done a little research, it's realistic to set goals because you know what's possible and you understand the challenges at hand.
Rand Fishkin gives a detailed and useful answer on his Whiteboard Friday video on SEO goals.
Here's a quick highlight:
1. Begin with your company's goals
2. Set marketing goals
3. Derive your global SEO goals from your marketing goals
4. And then decide on what metrics to track based on your SEO goals
You can see how, if you build these smart goals and you measure them correctly and you align them with what the company and the marketing team is trying to do, you can build something really special.
- Rand Fishkin, Co-Founder at Moz
3. Global SEO Keyword Research
Now that you have your goals, it's time to find the best keywords to target in your global SEO.
The first method to find keywords for your global SEO strategy is to use the tools that search engines provide to find some low competition keywords.
Seeing as you’re entering a new market, you want to find the lowest hanging fruits, and target those keywords first.
Google Keyword Planner is a free tool that you can use to find such keyword opportunities. This tool shows you Google’s data on search volumes for relevant keywords in your new geography.
Other options to consider include:
Remember, the figures from Keyword Planner, Yandex and Bing serve as your references. Don't take them as absolutes.
You should combine those figures with other research findings to make your final decisions.
When doing your keyword research, remember to refine by the specific country and language you're prospecting so you get the most accurate market data.
Another alternative is to use our keyword research tool. SEOptimer’s Keyword Research tool can be used to find the top keywords that you should target when entering a new market.
Marketers can use our tool to find keywords in more than 90 countries and several languages.
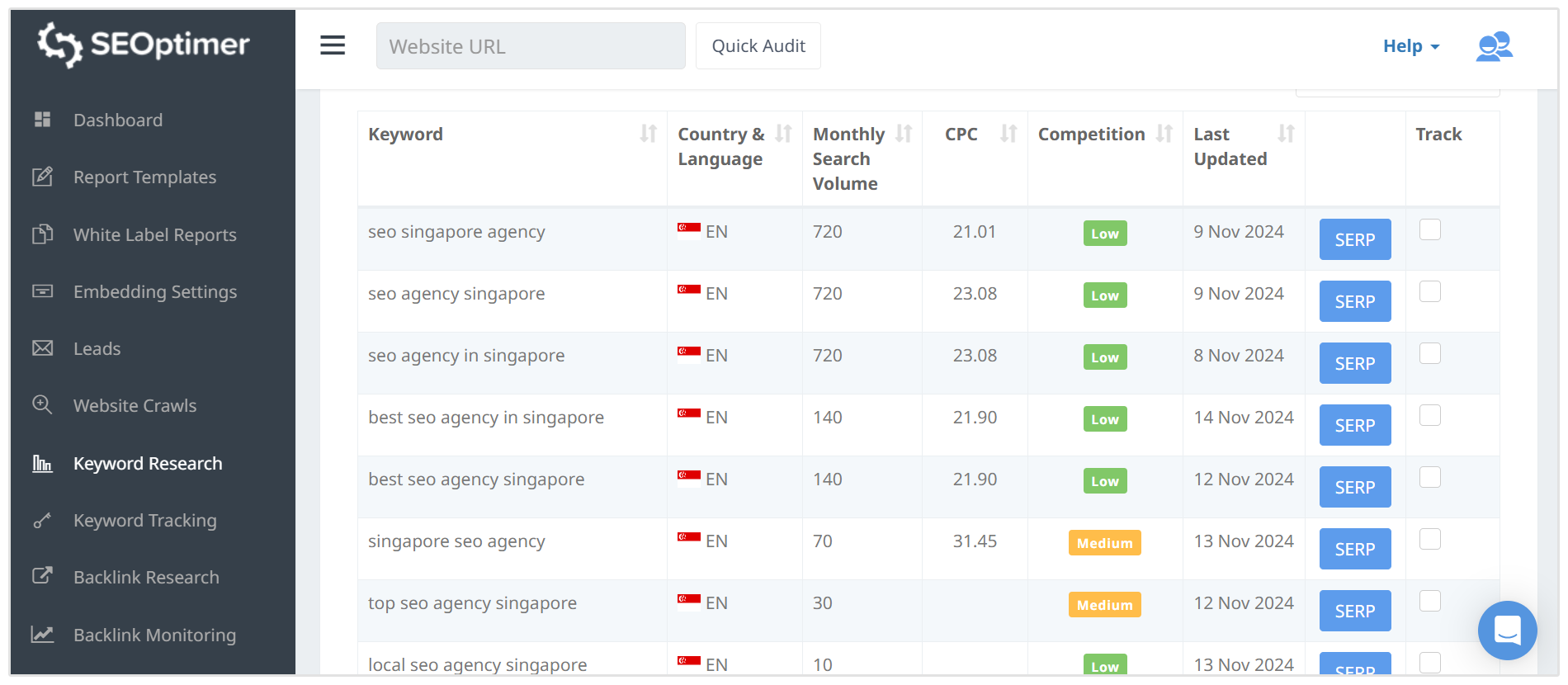
For instance, let’s say you provide SEO services in Australia and you want to expand your service offerings to Singapore.
With SEOptimer, you can find keyword opportunities for both English and Chinese (simplified) in Singapore.
In the below screenshot you can see that our tool shows "SEO agency Singapore" is a low competition keyword that has some decent search volume, you could target this keyword if you're expanding your agency's services into Singapore.
4. Study Your Competitor’s Global SEO Strategy
Competitor analysis does two critical things for you, it helps you know what you're up against and it opens your eyes to opportunities your competitors have found.
Other ways to know your competitors is through industry and market reports.
Who are the leaders in your space in those markets?
You can analyze their search traffic, backlinks and websites for strengths and weaknesses.
For this, I’d suggest using our Keyword Research tool to figure out who among your competitors already ranks for your target keywords.
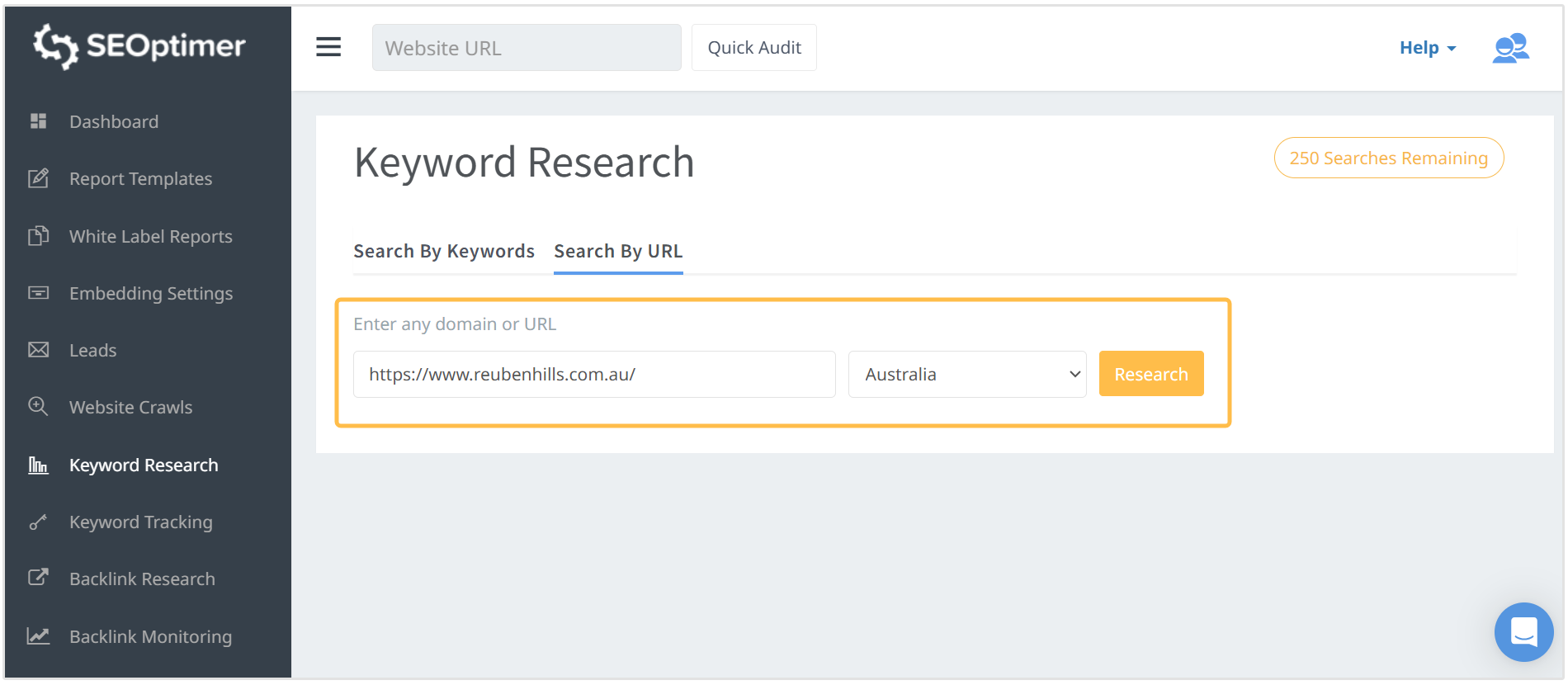
For instance, let’s say you own a coffee shop and you want to expand into the Australian market and one of the leading competitors there is Reuben Hills Coffee.
By plugging their URL into our Keyword Research tool, you can see all of the keywords that Reuben Hills rank for and are using on their website.
Note: Remember to change the Country and Language fields when you’re using our Keyword Research tool to study your competitor’s keyword strategy.
Plus, you can discover the sources of backlinks these competitors have and their rankings on search engines using our suite of SEO tools, mainly our Backlink Research and Keyword tracking tools.
5. Use Hreflang on Your Pages
The hreflang attribute tells search engines which language and region a specific webpage is intended for, helping users see the correct version of your site.
This is especially useful for multilingual or multi-regional websites.
To implement hreflang, you’ll need to add it to the <head> section of your page, the HTTP header, or your sitemap.
Each tag should reference all language versions of the page.
For example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://example.com/us/" /><link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr-fr" href="https://example.com/fr/" />
If your site targets a broader region, such as French-speaking West Africa, you can use a general language code (e.g., hreflang="fr") instead of country-specific ones.
Hreflang can help you:
- Serve the correct content to users based on their language or location.
- Avoid duplicate content issues by clarifying which version of a page to show.
E-commerce businesses often localize by country and language (e.g., Amazon US or Jumia Nigeria). On the other hand, tech services like Skype or Android focus on broader language targeting. Choose a strategy that aligns with your audience and business goals.
6. Decide on URL Structures

As I've noted earlier, location targeting is great for e-commerce businesses. But, depending on your unique business goals and your situation, you can implement location-based targeting to suit your audience's needs.
Your site structure could work with:
- ccTLD or gTLD domains
- Sub-directories
- Sub-domains

ccTLD and gTLD Domains
Using a ccTLD (e.g., .uk, .fr) is ideal if you have the resources to build separate site authority for each region.
However, ccTLDs require significant effort to establish visibility, and not all are treated equally by Google. For instance, .co and .me are considered gTLDs, not location-specific.
Before choosing ccTLDs, weigh the pros and cons carefully. They offer clear geographic targeting but demand high maintenance and SEO efforts for each domain.
Using Sub-Directories
Subdirectories (e.g., example.com/en-us/) are a great choice if you want to leverage the authority of your main domain. They simplify SEO by consolidating site authority under one domain.
For example, Electronic Arts (EA) uses subdirectories:
- US: https://www.ea.com/
- Canada: https://www.ea.com/en-ca
- Mexico: https://www.ea.com/es-mx
However, this approach can add complexity to site management, especially as your international presence grows.
At SEOptimer, we've elected to use this URL structure for our global SEO efforts. For instance, as you can see in the below screenshot, we are using https://www.seoptimer.com/it/ for our Italian language targeting.
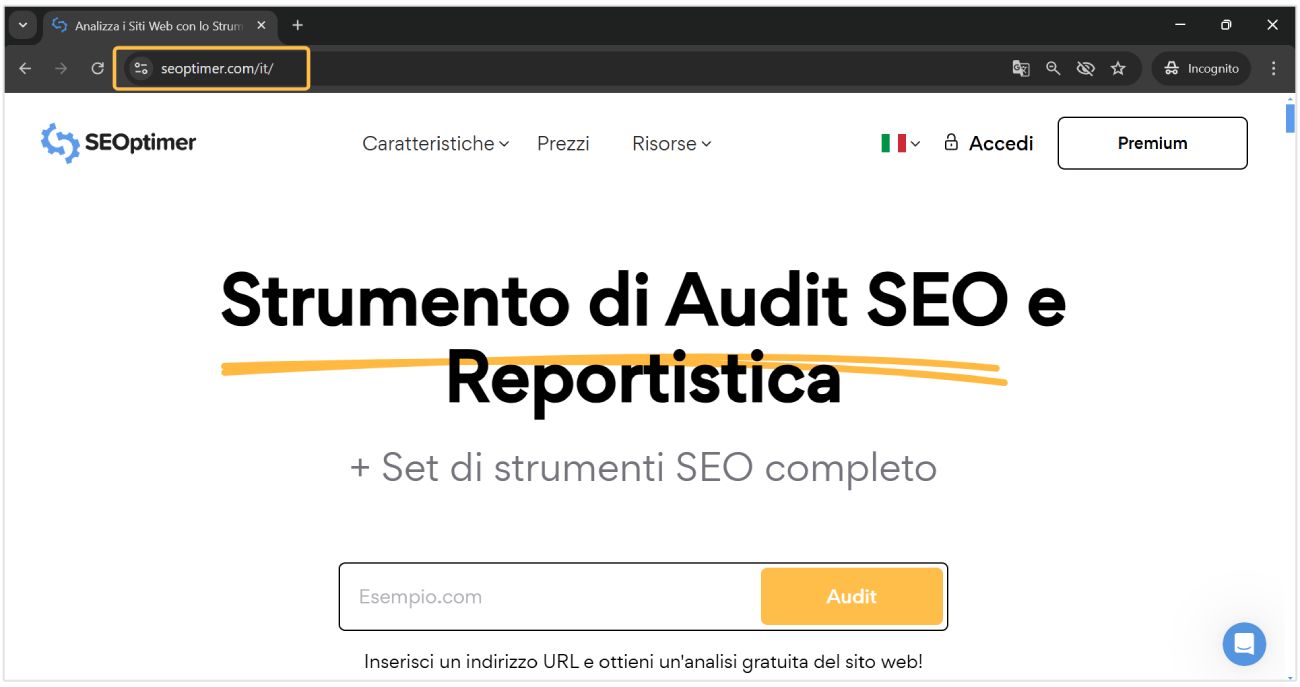
Using Sub-Domains
Subdomains (e.g., us.example.com) are an alternative if you want to isolate content for specific regions or languages while keeping it linked to your main domain. Like ccTLDs, subdomains often require separate SEO efforts since search engines treat them as semi-independent sites.
For example, Shop.com uses subdomains to target different regions:
- Hong Kong: hk.shop.com
- Canada: ca.shop.com
- Singapore: sg.shop.com

Choose the structure that aligns with your goals and resources. For e-commerce, ccTLDs often work well, while subdirectories or subdomains are more scalable for broader audiences.
7. Optimize for International Search Engines
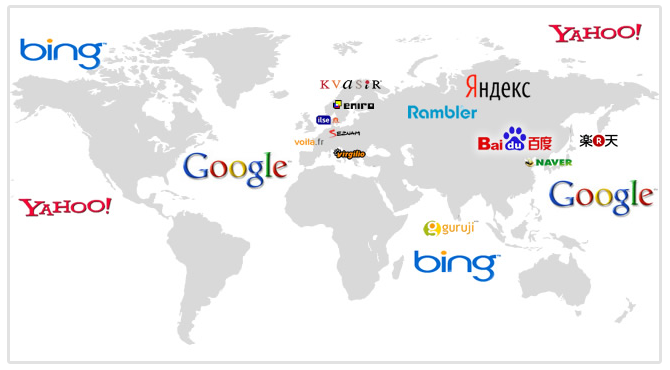
Some of the most developed international markets have strong preferences for other search engines apart from Google.
You can consider your global SEO incomplete if you haven't optimized for other search engines.
So you want to optimize for searches on the following search engines if you're targeting international audiences:
- Baidu: China
- Yandex: Russia
- Naver: South Korea
- Yahoo:Japan and South Korea
- Bing: US and many other markets
The first step here is to get an account with the relevant search engines that your target markets use. If these search engines use foreign languages you're not familiar with then use the help of a translator.
Next, get familiar with any unique features on these search engines' webmaster tools. If the search engines don't have English versions then you may need to pay for some help.
An option is to hire a webmaster who understands the local language or an SEO savvy translator to help you interpret your site's data.
8. Build a Robust Global SEO Backlinks Strategy
What's global SEO without link building?
As you probably already know, links are one of the two most important ranking factors for getting higher rankings. Links tell Google a whole lot about your site.
An abundance of links from a country would suggest that searchers from that country engage with your site's content.
Backlinks from authoritative sources also pass their authoritativeness to your site.
Links from a government, university, research institutions, national brand's website tells the search engines that your resource is credible and relevant to their audiences.
Social media links and mentions also influence your site's rankings. Lots of social mentions and shares from a particular country tells the search engines that your content resonates with audiences from that country. So how do you keep a robust backlinks strategy?
Use Competitors' Links for Inspiration
If your competitors are already doing well in your international markets, you can leverage their successes.
At LinkBuilder, we conduct competitor link analysis for our clients. For example, analyzing competitor backlinks was part of a strategy that led to a 5,329% traffic increase for PDF Simpli.
- Stewart Dunlop, Founder at LinkBuilder.io
I'd suggest adding your top competitors in each region to our Backlink Monitoring tool to keep an eye on your competitor's backlink profile. Our tool will notify you of any New Links and Lost Links that your competitors may have gotten.
For instance, the below screenshot shows all the New Links and Lost Links for Succulents and Sunshine, a blog in the gardening niche.
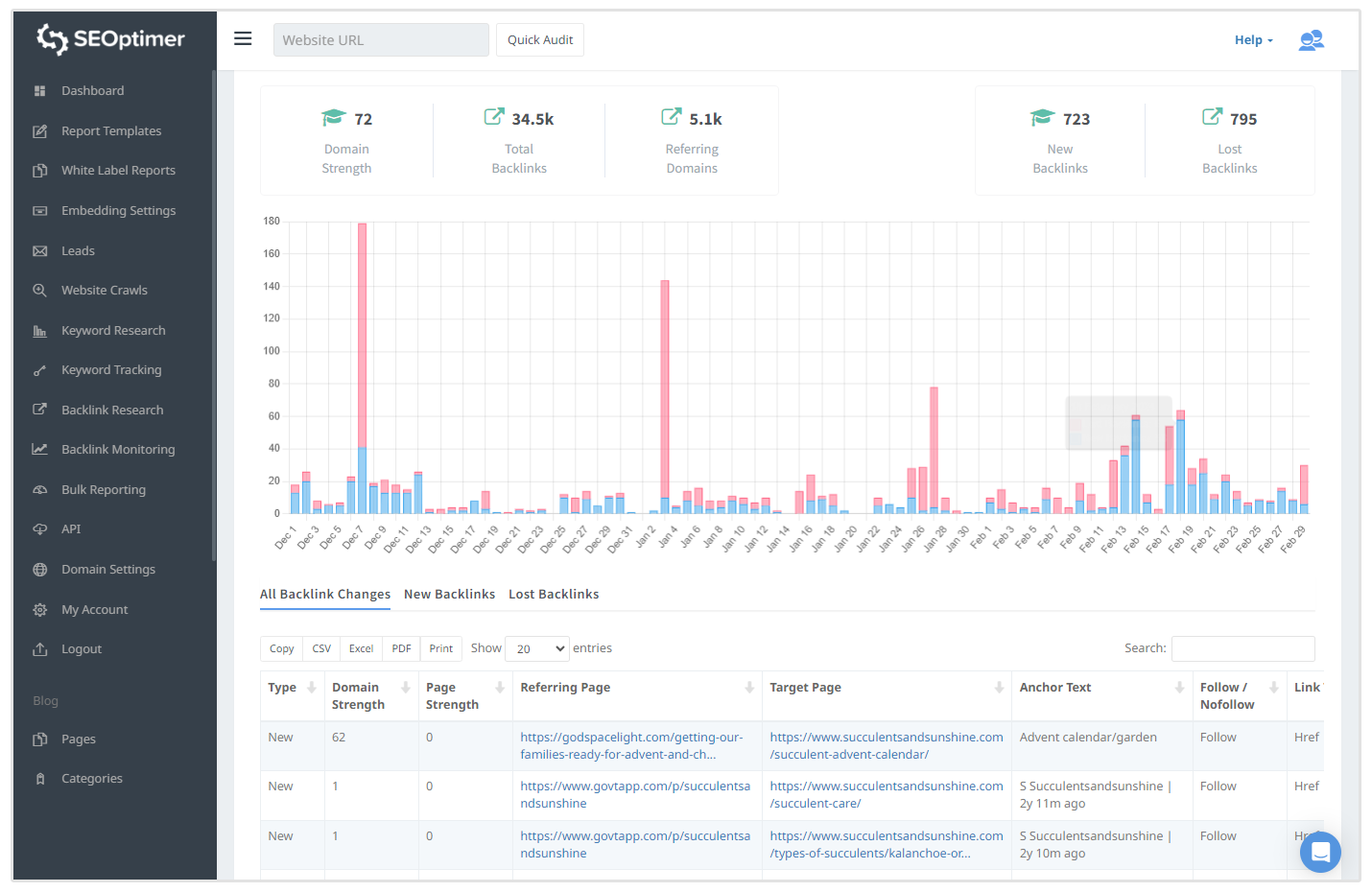
If your competitors' global SEO strategies are performing exceptionally well, then you should go beyond monitoring their links sources to adopt their link building strategies.
You can ask questions like:
- Do they use media promotions on TV and local newspapers to get a ton of attention?
- What influencers are they leveraging?
- What other strategies are they using to win links?
You want to experiment and then focus on top-performing local backlinks strategies. Prioritize getting backlinks from ccTLDs of the country or city you're targeting.
9. Measuring Your Global SEO Success
Tracking your global SEO efforts is crucial to understanding what works, what doesn’t, and where to focus on. Without measurement, you’re flying blind.
Here’s how to evaluate and refine your global SEO strategy effectively:
Set Clear KPIs
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) tailored to each target market. Audience behaviors vary by region, so your metrics should reflect these differences.
For example, in Japan, B2B decisions often involve group consensus, which may lengthen the sales cycle.
Essential KPIs to monitor include:
- Search rankings: Are your pages ranking for localized keywords?
- Organic performance: Track traffic, click-through rates, and impressions.
- User engagement: Monitor bounce rates, page dwell times, and conversions.
- Technical metrics: Evaluate site speed, mobile traffic, and indexed pages.
Localize Data Interpretation
Raw numbers only tell part of the story. Consider cultural nuances when analyzing data.
For instance, in some markets, colors or symbols might affect user decisions. A high bounce rate in one region might signal a cultural disconnect rather than a technical issue.
Take the time to understand how local traditions, norms, and beliefs influence behavior. This insight will allow you to make more informed decisions and avoid misinterpreting metrics.
Use Insights to Scale
Combine qualitative and quantitative data to refine your strategy and scale your business.
Insights from web analytics, paired with cultural understanding, help you identify growth opportunities and make region-specific adjustments to improve performance.
By consistently measuring and adapting, you’ll stay ahead in your international markets and maximize your global SEO success.
Global SEO Wrap Up
The opportunities you stand to enjoy from having a global SEO strategy are plentiful.
But your tactics can't be the same ones you use for traditional or local SEO.
Use this guide to help you start prospecting and dominating your industry on the international fronts.